


On July 18th, local time, U.S. President Donald Trump officially signed the “Guide and Establishment of the National Innovation Act on Digital Stability Coin” (referred to as the “Genius Act”), marking the United States’ first formal establishment of a regulatory framework for digital stable coins.
Since Trump took office in his second term, he has introduced several measures to support cryptocurrencies. What are the intentions behind the recent acceleration in legislative processes related to the Genius Act, and what impact will it have on the U.S. and global markets?
Accelerated Legislative Processes
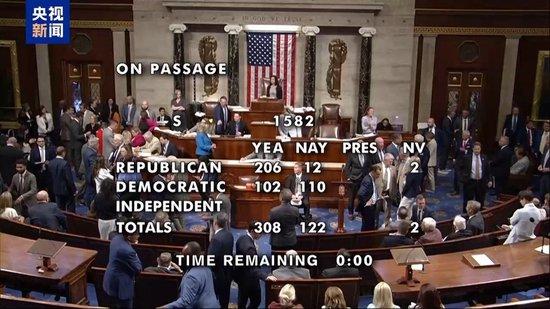
The Senate passed the Genius Act with 68 votes in favor and 30 against, marking the first approval of major cryptocurrency legislation by that body.
The House of Representatives voted to pass three bills related to stable coins and other cryptocurrencies.
“Guide and Establishment of the National Innovation Act on Digital Stability Coin”:
This bill aims to establish a regulatory framework for “anchored” stable coins. It requires stable coins to be supported by liquid assets such as U.S. dollars or short-term U.S. Treasury bonds, while also requiring issuers to disclose details of their stable coin reserves monthly.
“Clearing Act on the Digital Asset Market”:
The House also passed the bill with 294 votes in favor and 134 against, which will then be submitted to the Senate for consideration. The bill aims to clarify the regulatory scope of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, providing clear rules for the cryptocurrency market.
“National Act on Anti-Central Bank Digital Currency Surveillance”:
The bill was passed by the House Republicans with a majority in favor. It requires the Federal Reserve to prohibit the issuance of central bank digital currencies in the future, arguing that these would allow the federal government to monitor, track, and even control private financial transactions, thereby violating individual privacy and freedom. This bill also needs to be considered by the Senate, but due to significant controversy, it is difficult to ensure its final adoption.
△On July 18th, Trump officially signed the “Genius Act.”
The President of the United States, Donald Trump, officially signed the “Talent Act” at the White House and referred to it as one of the greatest transformations in financial technology since the internet’s inception. He also stated that he had signed an executive order to establish the “U.S. Strategic Bitcoin Reserve” and the “National Digital Asset Reserve,” and reiterated his stance on “absolutely not allowing a central bank digital currency to be established in the United States.”
Questions about U.S. Cryptocurrency-Related Bills
Why does the U.S. government push for cryptocurrency-related bills? What is the purpose behind the push for stablecoins? Can this goal be achieved?
What is a stablecoin? What makes it unique?
Answer: Stablecoins are pegged to the dollar and require U.S. assets for support.
Cryptocurrencies are generated through algorithms and operate on a decentralized model, meaning there is no central authority for issuance, with holders updating their holdings according to the algorithm.
The main cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin and stablecoins.
However, stablecoins differ from Bitcoin in that they are a type of cryptocurrency that maintains relatively stable prices, usually pegged to the dollar at a ratio of 1:1.
Following the signing and implementation of the “Talent Act,” stablecoins will be required to be supported by liquid assets such as the dollar or U.S. short-term bonds, and issuers will be required to disclose details of their stablecoin reserves monthly.
Currently, the two largest stablecoins globally are Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC), collectively accounting for about 90% of the total market value.
Stablecoins were first introduced in 2014. In 2020, the global market value of stablecoins was only $20 billion, indicating a preliminary stage in the market. Subsequently, stablecoins entered a rapid growth phase supported by two major drivers:
On one hand, in cryptocurrency transactions, over 90% of Bitcoin transactions are settled through USDT/USDC, making it the “crypto-dollar standard”;
On the other hand, in emerging markets like Argentina, stablecoins have become a “digital hedge asset” for the general public, accounting for up to 72% of the cryptocurrency trading volume in these countries.
According to the cryptocurrency data provider Binance, the stablecoin market is currently valued at approximately $247 billion. U.S. Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin stated that the stablecoin market is expected to grow to $3.7 trillion by 2030.
What is the purpose of the U.S. government’s push for stablecoins?
Answer: The U.S. government aims to maintain global monetary dominance.
Experts point out that in the development of digital currencies, the value and influence of the dollar have been significantly impacted. The U.S. hopes to leverage the model of promoting stablecoins to leverage the existing and strong advantages of the dollar,
maintaining and enhancing its influence in the field of stablecoins and digital currencies.
Trump and some officials have also suggested that through the issuance of stablecoins,
the fundamental purpose of the U.S. government’s push for stablecoins is to continue maintaining its leading position in both the global monetary system and payment systems, further affecting the future global monetary and payment systems, and maintaining America’s competitiveness.
Can the U.S. maintain its dollar status through stablecoins?
Answer: If the credibility of the dollar declines, stablecoins may also lose their appeal.
Expert analysis suggests that the current influence of the dollar globally is based on the post-World War II international economic order, forming its own international influence. The measures taken by the Trump administration show its disapproval of the U.S. trade deficit and its desire to maintain a surplus or balance. Maintaining a surplus means there will be less dollar flow into the international market through trade, which clearly restricts the use of dollars worldwide.
Experts indicate that whether a currency or a payment method gains favor is not just about the cost of use but also includes the reputation behind it.
Experts believe that the future of the United States’ ability to assume necessary responsibilities, fulfill commitments, and maintain the stability of the global economy through trade and economic relations, rather than intervening in international economic and trade relations through sanctions and long-arm jurisdiction, is crucial for the development of stablecoins.
If these measures are not achieved, merely changing the way US dollars are expressed without altering the underlying value determination method of the dollar, then it is likely that both the dollar and its corresponding stablecoins will struggle to gain global support in a more extensive manner in the future.
The bill has sparked continuous domestic debate within the United States.
After becoming law, the “Genius Bill” paves the way for banks to independently issue digital assets.
JPMorgan Chase CEO Jamie Dimon and Citigroup CEO Jane Fraser, among other Wall Street executives, are eager to explore the digital asset business. Bank of America CEO Brian Moynihan has reminded that it is currently unclear how much demand there is for digital currencies.
However, the bill has also faced skepticism and opposition from some members of both parties. According to CNN, some Democrats believe that the bill fails to provide adequate protection for consumers, national security, or financial stability, and accuse the Trump family of connections with cryptocurrencies. Republicans who oppose the bill argue that it does not follow an executive order signed by President Trump in January this year, which includes a ban on central bank digital currencies.
Stablecoins Face Criticism for Poor Performance
On June 24th, the International Clearing Union issued a stern warning, stating that
stablecoins have “performed poorly” in becoming widely used currencies.
The International Clearing Union identified three major deficiencies in stablecoins:
Firstly, they lack backing from a central bank;
Secondly, they lack sufficient safeguards against illegal use;
Thirdly, they do not offer flexibility in generating loans.
The institution reported, “Although the role of stablecoins in the future remains unclear, their performance in these three tests suggests that they might best serve as an auxiliary.”
Issuers of stablecoins claim that transferring money online using stablecoins is more convenient than through cross-border banks. However, the International Clearing Union believes that stablecoins can be held anonymously, aiding in the concealment of “black money.”
Furthermore, the Bank for International Settlements has highlighted that stablecoins face the risk of investors’ rapid redemptions. The Bank also warns that stablecoins could undermine currency sovereignty and trigger capital flight risks in emerging economies.
In addition to the warnings about stablecoin risks by the Bank for International Settlements, Christine Lagarde, President of the European Central Bank, also stated on June 23 that stablecoins are privately issued currencies, posing risks to monetary policy and financial stability.